Defensive stocks are equities of companies that exhibit resilience and stability during economic downturns, offering stable earnings and reliable returns. Such defensive companies typically belong to sectors such as utilities, healthcare, and consumer staples. They provide essential products and services that consumers continue to demand irrespective of prevailing economic conditions.
What is a Defensive Stock?
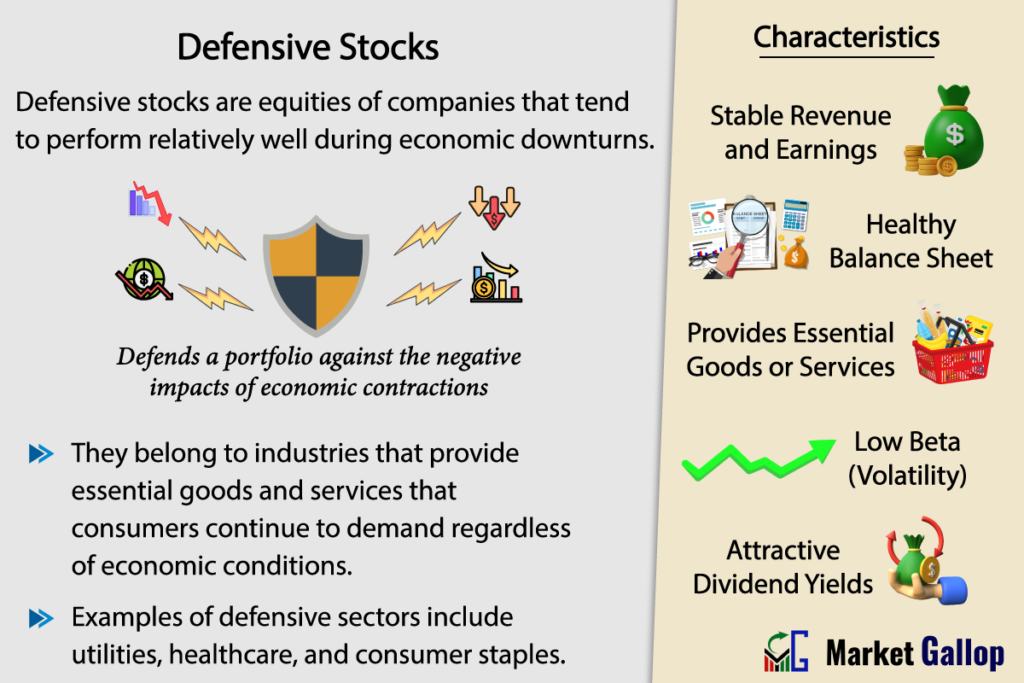
Defensive stocks refer to shares of companies that are considered resilient during economic downturns. These companies are able to generate stable revenue or earnings even in adverse economic circumstances. In general, they also provide reliable returns to investors (in terms of stock price appreciation) irrespective of the economic cycle. Many defensive stocks also have a history of providing regular and consistent dividend payments.
Defensive stocks are usually associated with industries that provide essential goods and services, which have relatively stable demand regardless of overall economic conditions. Hence, their ability to maintain performance during economic contractions, recessions, or market downturns.
Since their business performance is relatively unaffected by economic conditions, while other stocks may experience significant declines during recessions, defensive stocks typically exhibit more stability in terms of their stock prices. Therefore, during times of economic uncertainty, investors often turn to defensive stocks as a strategy to protect their portfolios.
As mentioned above, defensive stocks are typically found in industries that provide necessities or services that people continue to use even in challenging economic environments. As such, common defensive sectors include:
- Utilities: Companies providing essential services like electricity, water, and gas.
- Healthcare: Pharmaceutical companies, healthcare providers, and medical equipment manufacturers.
- Consumer Staples: Companies producing everyday necessities like food, beverages, and household products.
In general, the demand for the products or services of companies in the above sectors tends to remain relatively constant, even when consumer spending as a whole decreases during economic contractions.
Many defensive stocks are known for their consistent dividend payments. The consistent and often predictable nature of their cash flows allows them to maintain regular dividend payments, making them attractive to income-focused investors. This dividend-paying nature helps to provide a reliable income stream to investors even when stock prices may be under pressure.
Defensive Stock Definition
A defensive stock is a type of stock associated with companies that are considered resistant to economic downturns in terms of their business performance and share prices. These stocks belong to companies operating in industries that provide essential goods and services, leading to relatively stable demand even in challenging economic conditions.
Defensive stocks are sought after by investors for their perceived ability to “defend” a portfolio against the negative impacts of economic contractions, as they usually outperform the stock market during such periods.
Companies in defensive sectors often have steady and predictable cash flows. This financial stability allows them to weather economic challenges more effectively than companies with more variable revenue streams. For example, a pharmaceutical company tends to see consistent demand for its products, as people continue to require medical treatment regardless of economic fluctuations. On the other hand, companies in cyclical industries, such as automotive or luxury goods manufacturers, tend to experience variable demand, leading to fluctuating revenues depending on economic situations.
Defensive stocks typically have lower beta values, indicating lower volatility compared to the broader market. (Note: Beta measures a stock’s volatility in relation to the overall market.) This means that during periods of market turbulence or downturns, the price of a defensive stock fluctuates to a lesser extent compared to more cyclical or economically sensitive stocks. This characteristic makes them appealing to risk-averse investors who prioritize capital preservation.
Needless to say, investors often turn to defensive stocks as a strategy to mitigate risk and preserve capital during economic downturns or uncertain market conditions. During such periods, defensive stocks are considered a safer investment option due to their resilience and ability to provide consistent returns, including dividends.
Defensive stocks are also suitable for long-term investors looking for stability and consistent returns. While they may not offer the same high returns as growth stocks during economic expansions, they can provide a reliable foundation for a diversified portfolio.
It is worthwhile to note that while defensive stocks are generally less risky than more cyclical alternatives, they are not entirely immune to market fluctuations. Investors should still assess their risk tolerance and diversify their portfolios to include a mix of defensive and non-defensive assets.
Key characteristics that can be used to identify a defensive stock from other stocks include:
- Stable Revenue and Earnings: Defensive stocks typically demonstrate consistent revenue and earnings growth over time, even during economic downturns.
- Healthy Balance Sheet: Defensive companies usually maintain strong balance sheets with manageable debt levels, ample cash reserves, and stable cash flows.
- Low Beta: Defensive stocks are less sensitive to market fluctuations compared to others. These stocks tend to have a low beta value, indicating that they exhibit lower price volatility compared to the broader market.
- Provides Essential Goods or Services: Defensive stocks are associated with industries that provide essential goods or services that consumers continue to need regardless of economic conditions, such as healthcare, utilities, and consumer staples.
- Dividend Yield: Defensive stocks commonly offer attractive dividend yields, providing investors with a steady income stream regardless of market conditions.
Examples of Defensive Stocks
One well-known example of a defensive stock operating in the consumer staples sector is the Procter & Gamble Company (P&G). It is a multinational consumer goods corporation headquartered in Cincinnati, Ohio, United States. Founded in 1837 by William Procter and James Gamble, P&G has grown to become one of the world’s largest and most successful corporations, with a diverse portfolio of household, health, and personal care products.
Industry: Consumer Staples/Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG)
Products: P&G produces a wide range of everyday products, including household cleaning agents, personal care products, beauty and grooming products, and health and wellness items.
Reasons for Defensiveness
Stable Demand and Revenue: Products like shampoo, toothpaste, laundry detergent, and diapers are considered essential items, and demand for these products remains relatively stable, even during economic downturns.
Consumer Behavior: Consumers tend to continue purchasing these items regardless of economic conditions, making P&G less sensitive to economic cycles.
Consistent Dividend Payments: P&G has a history of providing consistent and reliable dividend payments to its shareholders, contributing to its status as a defensive stock.
Healthy Balance Sheet: P&G maintains a healthy balance sheet, with ample cash reserves and manageable debt levels, which is an indication of financial stability and robust management practices.
Some other well-known examples of defensive companies include:
- Johnson & Johnson (Healthcare)
- Colgate-Palmolive (Consumer Staples)
- NextEra Energy (Utilities)
Risk and Return of Defensive Stocks
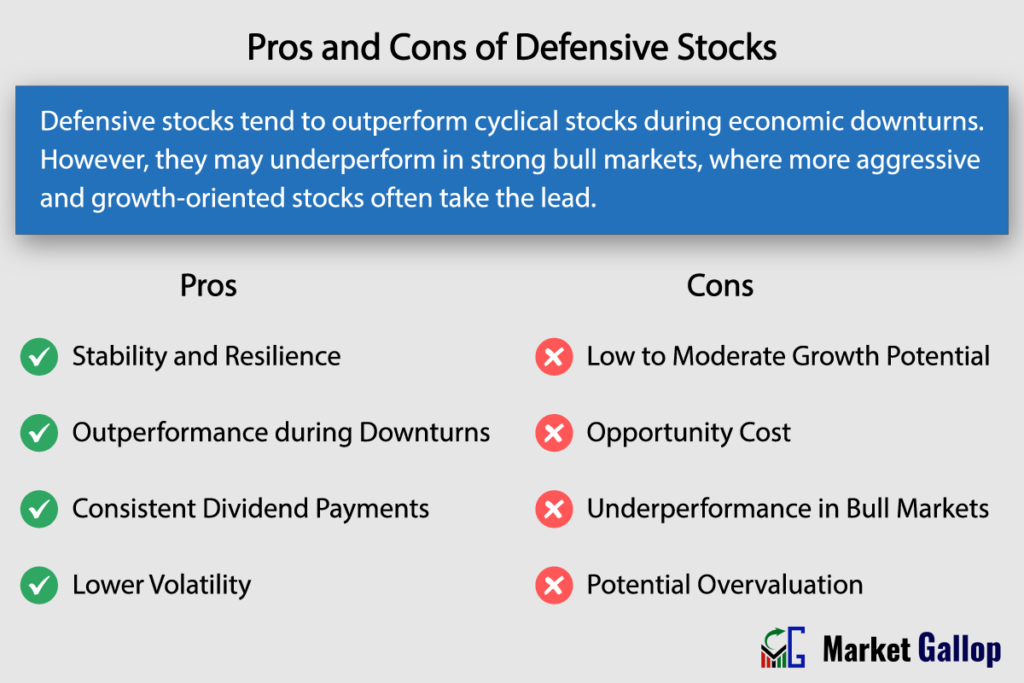
While defensive stocks may not offer the same level of high returns as more aggressive growth stocks during economic expansions, they do provide a moderate and steady growth profile. They are also known for their lower volatility compared to more cyclical or growth-oriented stocks. This lower volatility is attributed to the stable demand for the products or services these companies provide, which tends to be less influenced by economic fluctuations.
Risk
Low to Moderate Growth Potential: Defensive stocks offer low to moderate growth potential compared to more aggressive growth stocks. Hence, investors looking for high returns in a short period may find them less appealing.
Opportunity Cost: Investing heavily in defensive stocks may lead to missed opportunities for higher returns in more growth-oriented sectors, especially during periods of economic expansion.
Underperformance in Bull Markets: Defensive stocks may underperform in strong bull markets, where more aggressive and growth-oriented stocks often take the lead. Investors looking for high-risk, high-reward opportunities may find the returns from defensive stocks comparatively conservative.
Potential Overvaluation: In times of economic uncertainty, defensive stocks may become overvalued as investors flock to these safer options. This could lead to inflated stock prices, potentially impacting future returns.
Market Sensitivity: While defensive stocks are less sensitive to economic downturns, they may still experience market fluctuations. Changes in interest rates, regulatory environments, or industry-specific factors can impact their performance.
Interest Rate Risk: Defensive sectors such as utilities may be sensitive to changes in interest rates. Interest rates typically rise during times of economic distress. When interest rates rise, the dividend yields on defensive stocks may become less attractive relative to other investment options.
Return
Stability and Resilience: Defensive stocks are known for their stability and resilience during economic downturns. Their business models, often centered around providing essential goods and services, contribute to a consistent and stable demand.
Outperformance during Downturns: Defensive stocks tend to outperform more cyclical stocks during economic downturns. Their ability to maintain stable demand for essential goods and services makes them a preferred choice for investors seeking to mitigate risk during challenging economic conditions. Such investors seeking to protect their portfolios from market declines often allocate funds to defensive stocks to maintain stability.
Consistent Dividend Payments: Many defensive stocks have a history of providing regular and consistent dividend payments. This makes them attractive to income-focused investors seeking a reliable income stream, even during periods of market volatility.
Lower Volatility: Defensive stocks typically exhibit lower volatility compared to more cyclical or growth-oriented stocks. This lower volatility can be appealing to investors who prioritize capital preservation and are averse to significant market fluctuations.
Long-Term Performance: The appeal of defensive stocks lies in their ability to deliver steady, long-term performance. Investors holding defensive stocks may prioritize stability and preservation of capital over rapid capital appreciation.
Defensive Stock Sectors
Common defensive stock sectors include:
1. Consumer Staples
Characteristics: Companies in the consumer staples sector produce everyday necessities like food, beverages, personal care, and household products. Demand for these items remains relatively stable.
Examples: Procter & Gamble Company, Coca-Cola, Unilever.
Industries within the consumer staples sector include:
- Food Products: Companies involved in the production of packaged foods, including snacks, cereals, dairy products, and other food items. Examples include Nestlé and Kraft Heinz.
- Beverages: This includes companies that produce non-alcoholic beverages such as soft drinks, juices, and bottled water, as well as alcoholic beverages such as beer, wine, and spirits. Examples include PepsiCo and Coca-Cola.
- Household Products: Companies that manufacture and sell household goods such as cleaning products, detergents, paper products, and other household essentials. Examples include Procter & Gamble and Colgate-Palmolive.
- Personal Care Products: This category encompasses companies that produce personal care items such as soaps, shampoos, cosmetics, skincare products, and grooming products. Examples include L’Oréal S.A. and Johnson & Johnson.
- Tobacco: Companies involved in the manufacturing and sale of tobacco products, including cigarettes, cigars, and smokeless tobacco. Despite ethical considerations, tobacco stocks are often considered defensive due to the addictive nature of tobacco products, leading to stable demand. Examples include Philip Morris International, British American Tobacco, and Altria Group.
- Consumer Staples Distribution & Retail: Companies involved in the distribution and retail sale of the above consumer goods. Examples include Walmart, Costco Wholesale, and Dollar General.
2. Healthcare
Characteristics: Healthcare is considered a defensive sector because people continue to require medical services, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare products irrespective of economic conditions.
Examples: Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Merck & Co.
Industries within the healthcare sector include:
- Pharmaceuticals: Companies involved in researching, developing, manufacturing, and marketing pharmaceutical drugs and medications. Examples include Pfizer Inc. and Merck & Co.
- Biotechnology: Firms utilizing biological systems for diagnosing, treating, and preventing diseases, often focusing on genetic engineering and biopharmaceuticals. Examples include Amgen Inc. and Biogen Inc.
- Health Care Equipment and Supplies: Manufacturers of medical devices, equipment, and supplies used in diagnosis, treatment, and patient care. Examples include Abbott Laboratories and Medtronic plc.
- Health Care Providers and Services: Entities offering healthcare services directly to patients, including hospitals, clinics, and health insurance providers. Examples include UnitedHealth Group Incorporated and Anthem, Inc.
- Health Care Technology: Developers of technological solutions aimed at improving efficiency and outcomes in healthcare, such as electronic health records and telehealth platforms. Examples include Cerner Corporation and Teladoc Health.
- Life Sciences Tools & Services: It includes companies that provide various tools, equipment, and services to support research and development activities in the life sciences field, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and medical research. Examples include Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. and Illumina, Inc.
3. Utilities
Characteristics: Companies in the utilities sector provide essential services such as electricity, water, and gas. The demand for these services remains consistent, making utility stocks defensive.
Examples: Dominion Energy, NextEra Energy, Duke Energy.
Industries within the utilities sector include:
- Electric Utilities: Companies engaged in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity. They operate power plants, transmission lines, and distribution networks. Examples include Duke Energy Corporation and NextEra Energy, Inc.
- Gas Utilities: Companies involved in the distribution and transmission of natural gas. They operate pipelines, storage facilities, and distribution networks to supply natural gas to homes, businesses, and industries for heating, cooking, and other purposes. Examples include Dominion Energy, Inc.
- Multi-Utilities: These companies provide a combination of utility services, such as electricity, natural gas, and water, often serving as integrated utility providers. Examples include Exelon Corporation and American Electric Power Company, Inc.
- Water Utilities: Companies engaged in the treatment, purification, and distribution of water. Examples include American Water Works Company, Inc.
- Independent Power Producers & Energy Traders: These companies generate electricity using various sources such as renewable energy, coal, natural gas, and nuclear power. They may also engage in energy trading activities on wholesale markets. Examples include Enel S.p.A. and AES Corporation.
- Renewable Electricity: Companies involved in the generation of electricity from renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power. Examples include First Solar, Inc.
Special Mention: Energy
Are energy stocks cyclical or defensive? Please note that often energy sector stocks are classified as cyclical rather than defensive. This is because the demand for energy products, such as oil and gas, tends to fluctuate with economic conditions and industrial activity. Furthermore, the energy sector usually outperforms the market during periods of economic expansion.
However, MSCI (Morgan Stanley Capital International) classifies energy sector stocks as defensive based on their analysis of the sector’s performance in expansion and contraction periods within the business cycle.
So what are they: cyclical or defensive? When historical data is analyzed, it can be seen that energy sector stocks have exhibited characteristics of both defensive and cyclical assets at different time periods.
The energy sector encompasses companies involved in the exploration, production, refinement, and distribution of energy resources, including oil, natural gas, coal, and renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power.
Industries within the energy sector include:
- Energy Equipment & Services: It includes companies engaged in providing equipment, technology, and services to the energy industry. Examples include Halliburton Company and Schlumberger Limited.
- Oil, Gas & Consumable Fuels: It consists of companies primarily engaged in the exploration, production, refining, marketing, and distribution of oil, gas, and consumable fuels. Examples include Exxon Mobil Corporation, Chevron Corporation, and ConocoPhillips.
Special Mention: Telecommunications
Companies engaged in telecommunications services are an industry group included in the communication services sector. Since telecommunication companies provide essential communication services, including phone and internet services, historically it was considered a defensive sector.
However, in 2018, MSCI (Morgan Stanley Capital International) removed telecommunication services from its list of defensive sectors. The newly created communication services sector (which includes both telecommunication services and media & entertainment) was classified as a cyclical sector.
It is to be noted that some analysts still consider telecommunications services as defensive companies. This is because, even during economic downturns, demand for telecommunications services tends to remain relatively stable as people continue to require connectivity for work, education, and communication purposes.
Examples of telecommunications stocks include AT&T, Verizon Communications, and T-Mobile US.
Note: The above sectors are considered defensive because the products and services they offer are necessities, leading to more stable demand. However, it’s important to note that individual stock performance can vary based on company-specific factors and industry dynamics, so thorough research is essential for making informed investment decisions.
Defensive Stocks vs Cyclical Stocks
Unlike defensive stocks, cyclical stocks are associated with companies whose performance is closely tied to economic cycles. These stocks tend to perform well during economic expansions but may face challenges during downturns. They are often linked to industries highly dependent on economic conditions, such as manufacturing, construction, and travel.
As discussed already, the demand for the products and services of defensive stocks tends to remain consistent, as they are necessities irrespective of economic conditions. On the other hand, the demand for cyclical stocks is more variable, with higher demand during economic upswings when consumer spending is robust and lower demand during economic downturns.
Defensive stocks are favored by risk-averse investors seeking stability and consistent returns, especially during economic downturns. In contrast, investors with a higher risk tolerance and a positive economic outlook may favor cyclical stocks for their growth potential during economic expansions.
| Aspect | Defensive Stocks | Cyclical Stocks |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Stocks from sectors with stable demand regardless of economic conditions. | Stocks linked to industries highly dependent on economic cycles. |
| Business Characteristics | Demand remains consistent, as products and services are necessities. | Demand is variable, with higher demand during economic upswings. |
| Revenue and Earnings Stability | Generally stable and predictable | Typically experience fluctuations based on the business cycle. |
| Stock Performance in Economic Cycles | Outperform other stocks or the market as a whole during economic downturns. | Perform well during economic expansions but typically face challenges in downturns. |
| Beta Value | Typically lower beta values, indicating lower volatility. | Typically higher beta values, indicating higher volatility. |
| Dividend Payments | Often known for consistent dividend payments. | Depends on other factors and the individual company. |
| Investor Strategy | Favored by risk-averse investors seeking stability. | Attractive to investors with higher risk tolerance and positive economic outlook. |
| Examples | Johnson & Johnson (healthcare), The Procter & Gamble Company (consumer staples), Dominion Energy (utilities). | Ford (automotive), Caterpillar Inc. (construction), Delta Air Lines (travel and leisure). |